Brass is an alloy primarily made up of copper and zinc, with varying proportions of these two metals to create different types of brass, each with unique properties. Brass is widely used in various applications due to its excellent combination of strength, ductility, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal.
Key Components of Brass:
- Copper (Cu): Copper is the primary component in brass, typically making up between 55% to 95% of the alloy. It gives brass its strength, malleability, and corrosion resistance.
- Zinc (Zn): Zinc is the second primary component, and its proportion usually ranges from 5% to 45%. The amount of zinc in brass influences its hardness and workability. The higher the zinc content, the stronger and more brittle the brass tends to become.
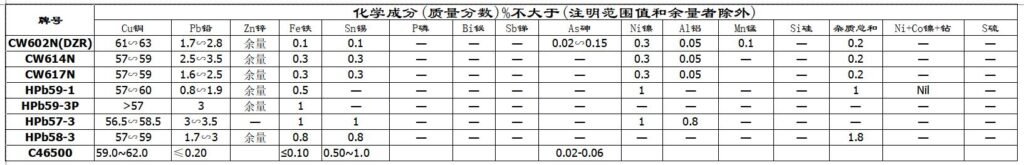
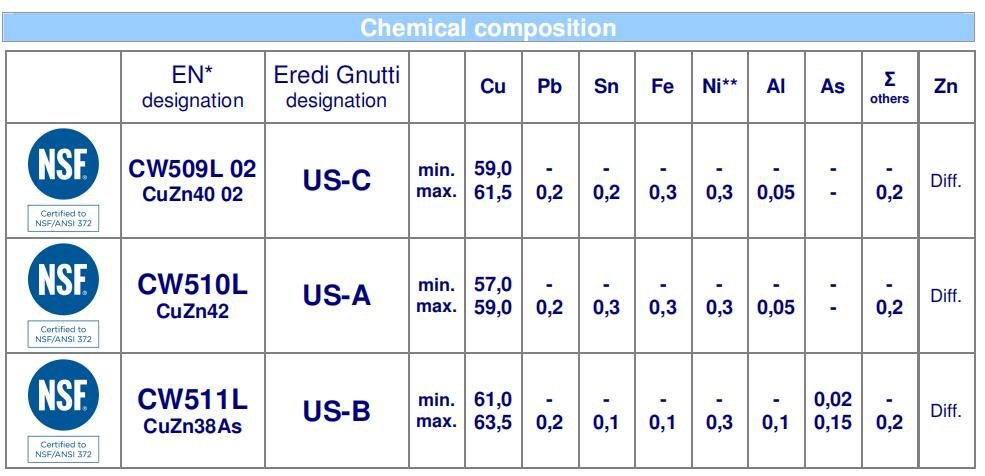
- CW602N See the detail performancehttps://www.eredignutti.it/en/product/cw602n/
- CW614N See the detail performancehttps://www.eredignutti.it/en/product/cw614n/
- CW617N See the detail performancehttps://www.eredignutti.it/en/product/cw617n/
- CW509L See the detail performancehttps://www.eredignutti.it/en/product/cw509l/
- CW511L See the detail performancehttps://www.eredignutti.it/en/product/cw511l/
Why Brass is Used:
Brass is a versatile material, offering a combination of benefits that make it useful in many industries. Here are some of the key properties and reasons for its popularity:
- Corrosion Resistance: Brass is highly resistant to rust and corrosion, making it ideal for use in environments that expose materials to moisture, such as plumbing, marine equipment, and electrical components.
- Ductility and Malleability: Brass can be easily shaped, formed, and machined into different shapes without cracking. This makes it ideal for creating complex and intricate parts, such as fittings, valves, and decorative elements.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Brass has a bright, golden-yellow appearance that makes it aesthetically pleasing, which is why it’s often used in jewelry, musical instruments, and architectural details.
- Electrical Conductivity: Brass has good electrical conductivity, although it’s not as conductive as pure copper. It is commonly used in electrical connectors, contacts, and switches.
- Low Friction: Brass has a low coefficient of friction, which makes it ideal for use in moving parts, such as in locks, gears, and valves, where smooth movement is required.
- Non-sparking: Brass does not produce sparks when struck against other materials, making it a safe choice for use in environments where sparks could lead to hazardous situations, such as in explosive or flammable atmospheres.

Types of Brass:
There are several types of brass, each with distinct properties based on its composition and intended use:
- Alpha Brass (Single-phase): This type of brass contains up to 37% zinc and is the most malleable. It’s used in applications that require good machinability and formability, such as musical instruments, coins, and decorative hardware.
- Beta Brass (Two-phase): Contains more than 37% zinc and has a stronger, harder structure compared to alpha brass, but it is less malleable. Beta brass is used for heavy-duty applications such as marine fittings and industrial machinery parts.
- Alpha-Beta Brass (Mixed-phase): This type has a mixture of both alpha and beta phases and contains about 35% to 45% zinc. It offers a balance of strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance. It is commonly used in plumbing fittings, valves, and automotive parts.
- Leaded Brass: Brass alloys with small amounts of lead (usually around 1-3%) to improve machinability. Leaded brass is often used in plumbing fittings and valves, where complex machining is needed.
- Naval Brass (C46500): A special type of brass containing about 1-2% tin in addition to copper and zinc. It has excellent corrosion resistance in marine environments and is used for shipbuilding and marine hardware.
- Free-Cutting Brass: These are brass alloys with higher levels of lead, specifically designed for ease of machining. It’s commonly used in the production of complex mechanical parts.
Applications of Brass:
Due to its many favorable properties, brass is used in a wide variety of applications across different industries:
- Plumbing: Brass is commonly used in plumbing fittings, valves, faucets, and pipes due to its corrosion resistance and strength.
- Electrical: Brass is used in electrical connectors, terminals, and switches because of its conductivity and ability to resist corrosion.
- Automotive: Brass parts such as radiator components, fittings, and bushings are used in the automotive industry.
- Musical Instruments: Many wind instruments (such as trumpets, trombones, and saxophones) are made from brass due to its resonant qualities and ease of shaping.
- Decorative Items: Because of its golden color and aesthetic appeal, brass is often used in jewelry, hardware, and decorative fixtures.
- Marine: Brass is used in the marine industry for parts exposed to seawater, such as boat fittings, propellers, and engine components, especially alloys like naval brass (C46500).
Summary:
Brass is a versatile and durable alloy made primarily of copper and zinc. Its wide range of properties, including corrosion resistance, machinability, strength, and aesthetic appeal, makes it an excellent choice for many industries. From plumbing and electrical components to musical instruments and decorative items, brass plays a crucial role in a variety of applications. The specific composition of brass can vary depending on the required characteristics, such as the amount of zinc or the addition of other elements like lead or tin.
Choose IVALVECRAFT, choose reliable partner, enjoy the high quality and best service.


