Choosing the right valve size is crucial for ensuring optimal performance in your plumbing or heating systems. A wrong-sized valve can lead to leaks, reduced efficiency, or even system failure. These issues can cause costly repairs and downtime, especially for businesses relying on consistent operations. But don’t worry—this guide will walk you through the steps to accurately check valve size, ensuring you get the perfect fit every time.
To check valve size, you need to measure the valve’s dimensions, including its diameter, stem size, and flow capacity. This involves using tools like calipers, tape measures, or valve sizing charts. Proper sizing ensures compatibility with your system and avoids performance issues.
Understanding how to measure and calculate valve size is essential for anyone involved in plumbing, heating, or industrial systems. Let’s dive deeper into the specifics to help you make informed decisions.
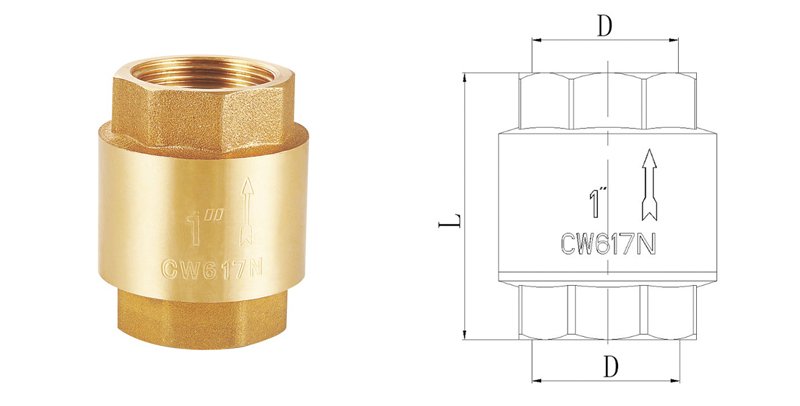
How to Measure Water Valve Size?
Measuring water valve size is the first step in ensuring compatibility with your system. Start by identifying the valve type—whether it’s a ball valve, gate valve, or thermostatic radiator valve. Each type may have slightly different measurement methods, but the basics remain the same.
- Measure the Diameter: Use a tape measure or caliper to determine the inner diameter (ID) and outer diameter (OD) of the valve. For threaded valves, measure the thread size, which is often expressed in inches (e.g., 1/2″, 3/4″).
- Check the Valve Body: Look for markings or labels on the valve body that indicate its size. Many manufacturers stamp this information directly on the product.
- Use a Valve Sizing Chart: If you’re unsure, refer to a valve sizing chart that matches your valve type. These charts provide standard dimensions for various valve sizes.
Accurate measurement ensures that the valve will fit seamlessly into your system, preventing leaks or flow restrictions.
How Do You Calculate Valve Capacity?
Valve capacity, also known as flow capacity, determines how much fluid can pass through the valve at a given time. This is critical for maintaining system efficiency and avoiding bottlenecks.
- Understand Cv Value: The Cv (flow coefficient) value is a standard measurement of valve capacity. It represents the flow rate of water (in gallons per minute) at a pressure drop of 1 psi.
- Use the Formula: To calculate the required Cv value for your system, use the formula:
Cv = Q / √(ΔP/SG)
Where:
- Q = Flow rate (GPM)
- ΔP = Pressure drop (psi)
- SG = Specific gravity of the fluid
- Consult Manufacturer Data: Most valve manufacturers provide Cv values for their products. Match your calculated Cv with the manufacturer’s specifications to select the right valve.
Calculating valve capacity ensures that your system operates efficiently, even under maximum load.
How Do You Measure Valve Stem Size?
The valve stem is a critical component that controls the opening and closing of the valve. Measuring its size is essential for replacements or upgrades.
- Identify the Stem Type: Valve stems can be threaded, smooth, or have other configurations. Determine the type before measuring.
- Measure the Diameter: Use a caliper to measure the stem’s diameter. This is typically expressed in millimeters or inches.
- Check the Length: Measure the stem’s length from the base to the tip. This ensures compatibility with the valve body and actuator.
- Refer to Valve Parts Diagrams: If you’re unsure, consult a valve parts diagram to identify the stem’s dimensions and its relationship with other components like the valve assembly or control valve parts.
Accurate stem measurement ensures smooth operation and extends the valve’s lifespan.
Summary
Checking valve size is a straightforward process if you know what to measure and how to calculate key parameters like diameter, capacity, and stem size. By following the steps outlined above, you can ensure that your valves are perfectly suited to your system’s needs, avoiding costly mistakes and downtime.
Choose IVALVECRAFT, choose reliable partner, enjoy the high quality and best service.


